Turkey is located in an active seismic zone, making it prone to earthquakes. Turkey is a region of intense rupture and slip movements during the aphetic Alpine-Himalayan orogenesis between the continents of Europe, Anatolia and Arabia. These movements have led to the identification of Turkey as an earthquake-prone region, located on layers of the earth's crust with great earthquake potential.
In addition to the fact that Turkey's crust is subjected to opening and sliding movements, the earthquake potential is increased by the fact that crustal fault lines are located in many regions. For this reason, Turkey is recognized as an earthquake zone and is therefore an important country in terms of earthquake management and disaster preparedness systems.
Also Read: US Army Shoots Down Flying Object Near Lake Huron
Turkey's Earthquake Zones
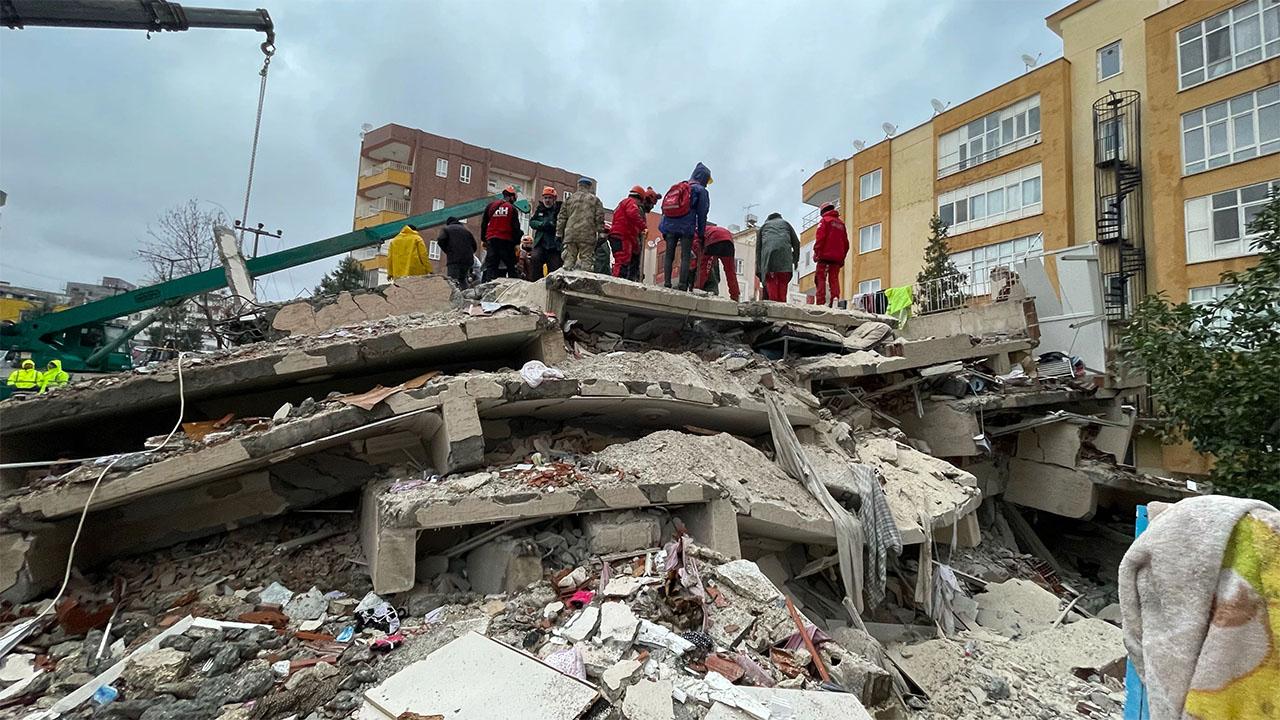

North Anatolia Earthquake Zone
The North Anatolian earthquake belt extending in the east-west direction in the northern part of Turkey has a length of approximately 1500 km. It starts from the Saros Gulf in the Marmara Region and extends to the Aras Valley in the Eastern Anatolia Region. The KAF system shows high seismic activity due to the fact that the Anatolian Block is between the Arabian Plate in the south and the Eurasian Plate in the north and therefore moves rapidly in the form of westward opening.
Southeast Anatolia Earthquake Zone
It extends in an arc from the Gulf of İskenderun to the east of Van. Hatay, Kahramanmaraş, Adıyaman, Malatya, Elazığ, Bitlis and Van are in this belt. This fracture line connects with the North Anatolian earthquake belt around Bingöl-Karlıova. Frequent earthquakes also occur around Lake Van and on faults in the Malazgirt, Tutak (Ağrı), Aşkale-Erzurum-Pasinler-Horasan basins to the north.
Western Anatolia Earthquake Zone
There are some major fault lines extending along the Bakırçay, Gediz, Küçük and Büyük Menderes depression plains in the Aegean Region. The earthquake zone, which is compatible with these fault lines, includes Ayvalık, Dikili, İzmir, Aydın, Denizli, Isparta and Akşehir. Faults also extend along the edges of the Burdur and Acıgöl basins and the northern foothills of the Sultan Mountains. Earthquakes occur from time to time along these faults.
Which Type of Earthquake is Common in Turkey?
Earthquakes can be of different types according to their causes. The earthquakes in Turkey are mostly tectonic earthquakes. The second type of earthquakes are volcanic earthquakes. These occur as a result of the eruption of volcanoes. It is known that such earthquakes are caused by the explosions of gases formed as a result of physical and chemical events during the ascent of molten matter deep in the earth. Since they are related to volcanoes, they are localized and do not cause significant damage.
A tectonic earthquake is the most common type of earthquake caused by plate cracking in the Earth's crust. Tectonic earthquakes occur when different parts of the earth's crust move relative to each other and crack. As a result of these cracks, the energy of the earth's crust is suddenly released and this energy spreads through the earth's crust as earthquake energy. This energy causes ground shaking or earthquake waves. Tectonic earthquakes can occur in many parts of the world and can cause serious damage and loss.
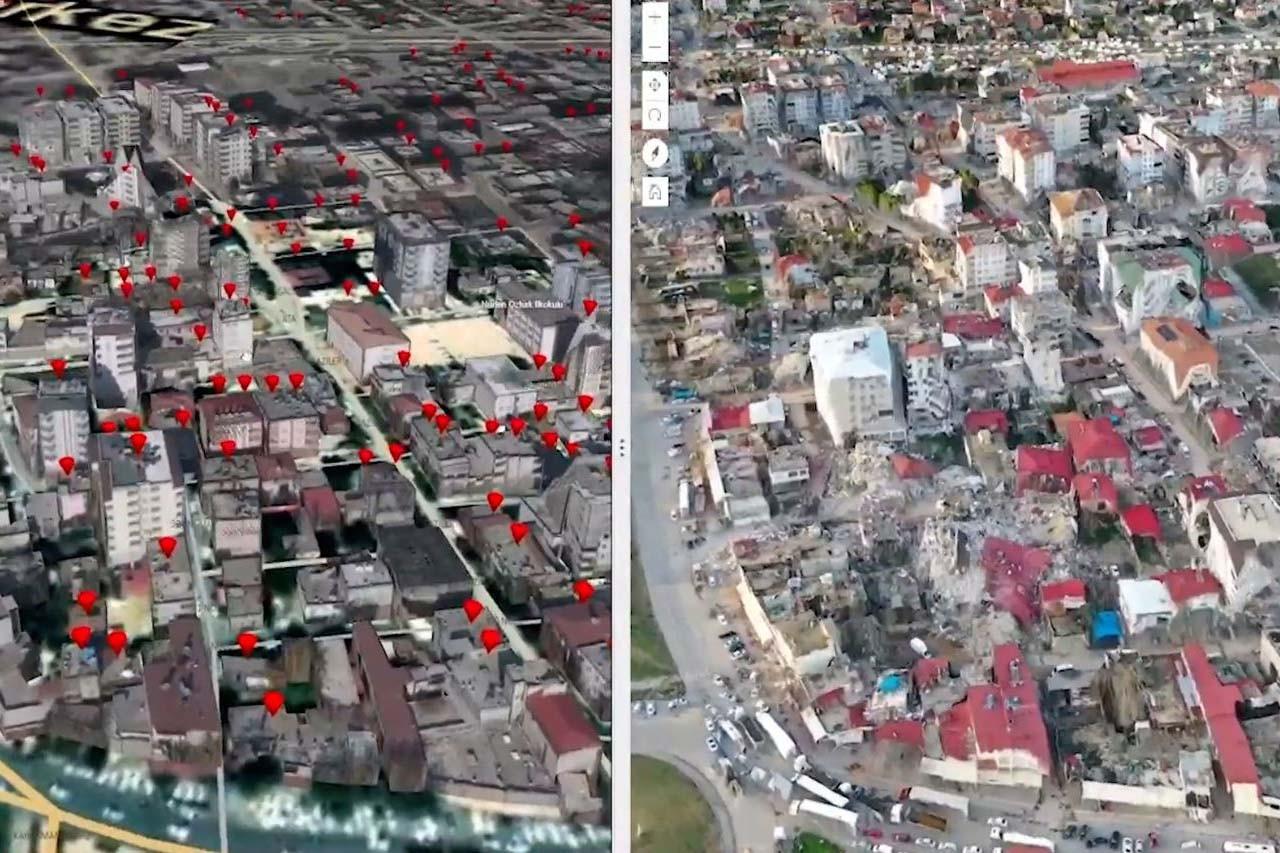




No comments yet for this news, be the first one!...